Cell-derived nanoparticles
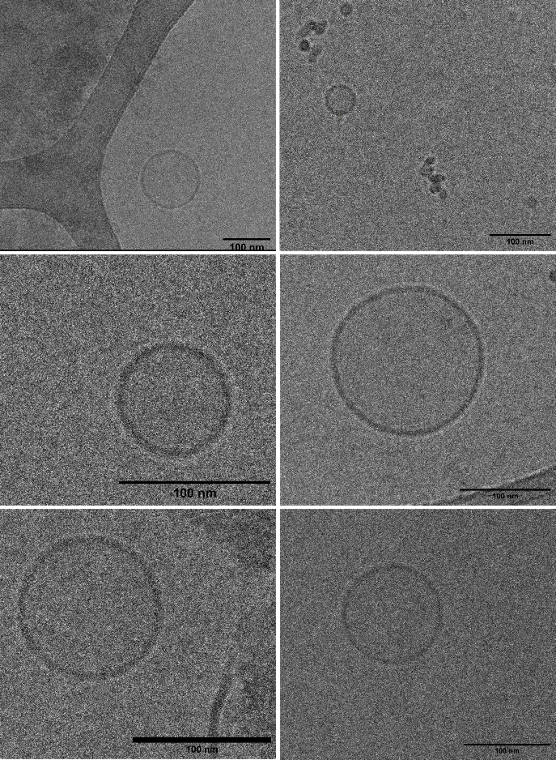
Cell-derived nanoparticles include a diverse array of nanoscale structures originating from various cell types (cell ghosts, exosomes, lipid-based and peptidic nanoparticles), each exhibiting unique properties. These nanoparticles maintain the biological properties of their parent cells, making them promising candidates for targeted drug delivery, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications in the fields of oncology and regenerative medicine.
One of the most significant applications of cell-derived nanoparticles is in the development of targeted drug delivery systems. These nanoparticles can encapsulate therapeutic agents (like antibiotics in our applications) and deliver them specifically to diseased cells, minimizing side effects on healthy tissues.
Nevertheless, we are interested in expanding their portfolio of applications beyond the state of the art, and explore their use in active immunization against infectious diseases. The philosophy behind this approach is that nanoparticles themselves will be the active drug (nano-vaccine), and not just a delivery system.
The team working on the project
The sponsors of the project





